The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a regulation of the European Union (EU) that aims to regulate the use of personal data of individuals and protect their rights.
For businesses, compliance with the GDPR is essential not only to avoid fines but also to gain customers' trust.
Here are some obligations to help businesses comply with the GDPR effectively:
1. Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
The DPO oversees the company's data protection compliance.
The GDPR requires certain businesses to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to the competent supervisory authority (CNIL for France).
To learn how to appoint a DPO on Dastra, click here.
Note:
The appointment of a DPO is mandatory for:
- Companies that process 'sensitive' data or data relating to criminal convictions and offenses on a large scale;
- Public authorities or bodies (except for courts when acting in their judicial capacity);
- Companies that, as part of their processing of personal data, carry out regular and systematic monitoring of individuals on a large scale.
Outside of these three cases, it is strongly recommended to appoint a DPO.
This allows entrusting an expert with the identification and coordination of actions to be taken regarding personal data protection. The DPO can be internal or external to the company. It can also be a shared role (especially in the public sector).
Consult our article on the methods of appointing a DPO to ensure you designate the right person.
2. Develop a data mapping of the company
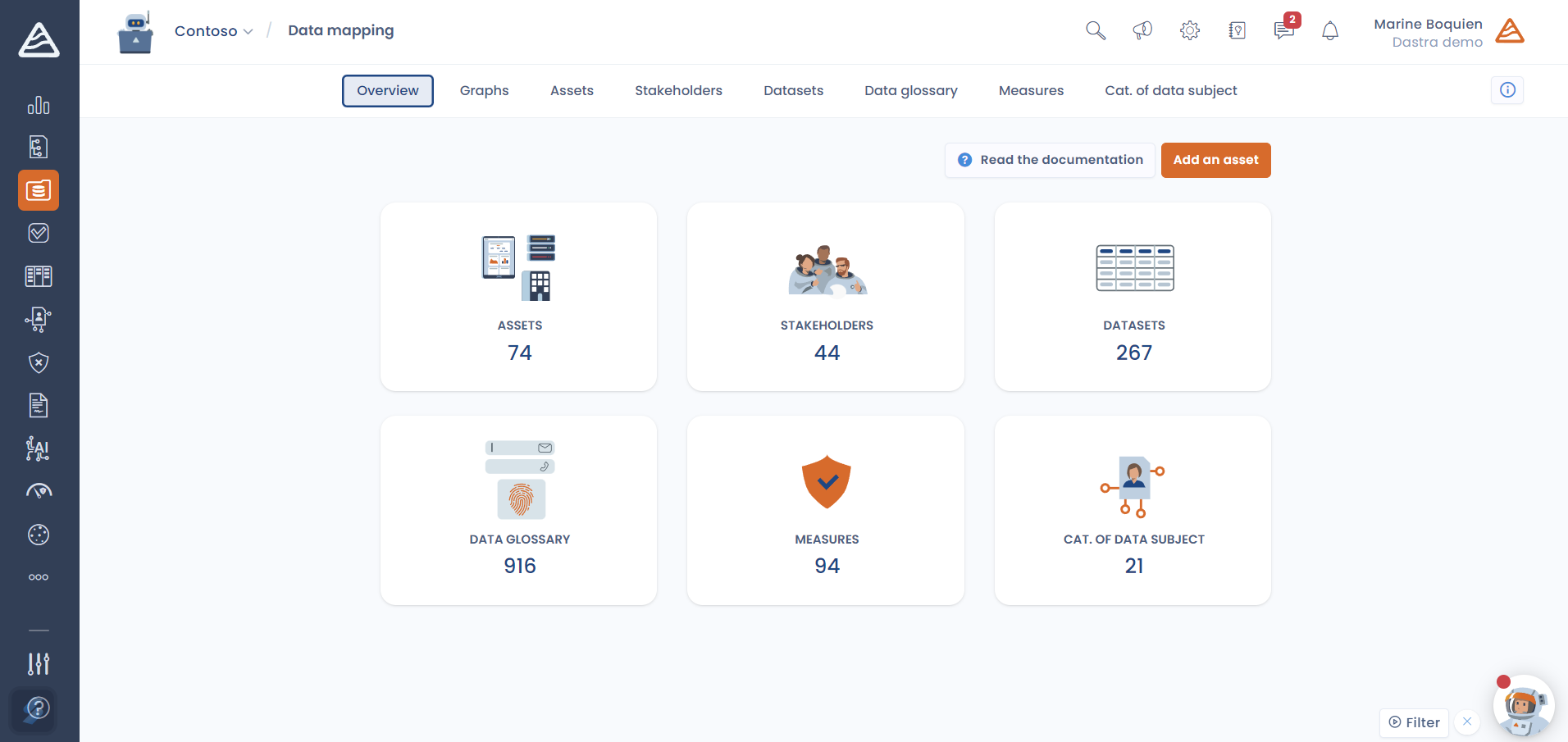
What tools store and process personal data? Personal data is omnipresent in CRMs, email software, mailboxes, etc. It is essential to exhaustively list all the tools used, whether digital or not.
What types of data are present in these tools? The data can be obvious, such as the name and surname, or more subtle and indirect, such as a phone number, a customer number, a date of birth, etc. It is important to note that all information allowing the direct or indirect identification of a natural person is considered personal data according to Article 4 of the GDPR.
It is also crucial to recall that personal data includes all information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person, whether directly (e.g., name and surname) or indirectly (e.g., social security number, email address, conversation recordings).
Note that even in the context of a B2B relationship, personal data exists because behind every company, there is always a natural person.
In this context, personal data can be linked to the professional email address and the identity of the natural person representing the company.
3. Analyze and assess risks
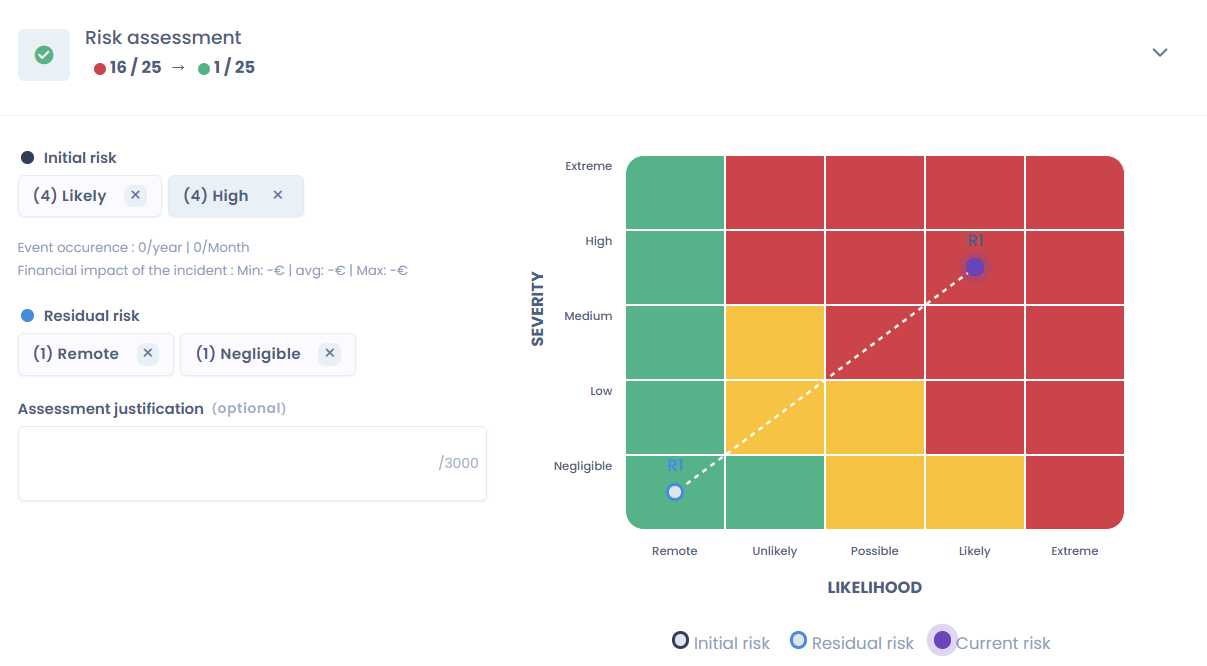
Once the data is mapped, it is necessary to analyze the risks associated with its processing.
This analysis includes assessing the security of information systems, data processing processes, and data protection policies.
This step allows identifying vulnerabilities and implementing measures to mitigate them.
What elements present a compliance risk for individuals whose personal data is processed?
- Retention period: For example, keeping surveillance video images beyond one month may pose a problem.
- Data collection: If you purchase email databases for commercial actions, individuals' consent may not have been properly obtained, which could result in reports to the CNIL.
- Identification of sensitive data: For instance, if you collect information about a person's sexual orientation in a survey, appropriate security measures should be taken, such as restricted access to the results or pseudonymization.
- Subcontractors: If you use non-GDPR compliant no-code tools from the United States, this can also be problematic.
This list is not exhaustive. Various risks may arise in the course of your activities. The important thing is always to consider how to reduce these risks to an acceptable level.
Bear in mind that when there is a high risk to individuals' rights and freedoms, it is necessary to carry out an impact assessment, known as a 'PIA' or 'DPIA'.
Did you know? With Dastra, you have the ability to conduct data protection impact assessments. Quickly identify targeted processing activities and easily meet the requirement to assess privacy risks.
Discover this feature by clicking the button below:
4. Build a record of processing activities
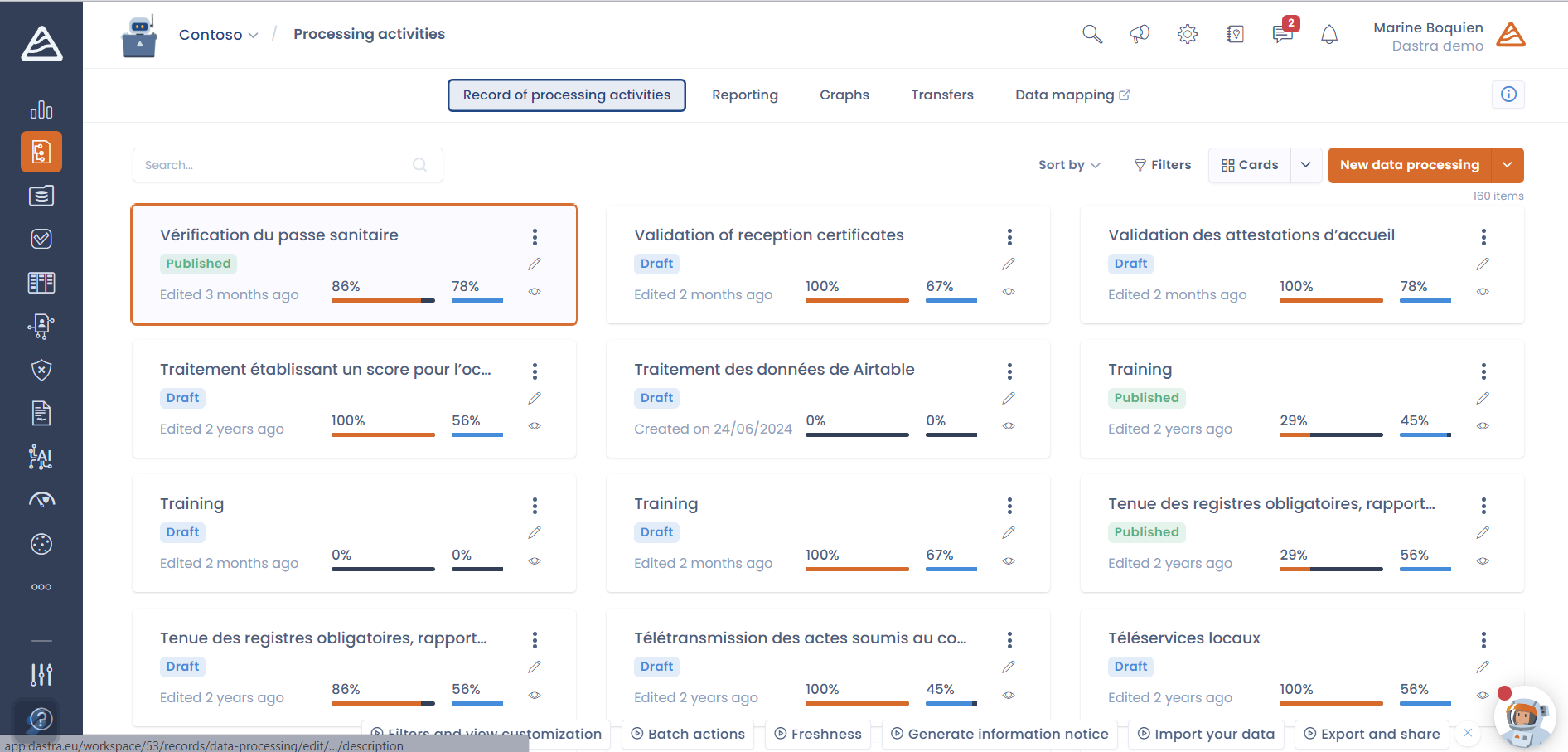
The record of processing activities is an essential document listing all processes involving personal data.
These processes include various operations such as collection, recording, use, transmission, pseudonymization, and destruction of data. Each operation on personal data is considered a processing activity.
Within the register, it is necessary to provide several pieces of information for each processing activity:
Purpose of data collection: Each collected data must have a specific purpose, guiding its use. If data is not used in accordance with this purpose, it is advisable to remove it from the database.
Legal basis for collection: Each data collection must be authorized, whether by the consent of the concerned individual, legal obligations, contracts, or legitimate interests. The legal bases for collection are defined in Article 6 of the GDPR.
Data retention period: The data retention period must be justified based on the purpose of the processing. The CNIL provides a reference framework to help determine this duration.
Persons with access to data: It is important to identify authorized recipients with access to the data, including subcontractors. Only competent persons should have access to the data.
Implemented security measures: Security measures must be implemented to ensure data protection.
5. Develop and update privacy policies
This document is now essential! It informs your users, customers, and partners about how you manage their personal data and the measures taken to ensure its protection.
Privacy policies must be transparent and easily accessible. They should clearly explain:
- The reasons for data collection;
- The specifics of the processing activities performed;
- The procedures for exercising their rights;
- The list of subcontractors, etc.
It is important for these policies to be reviewed and updated regularly.
6. Implement technical and organizational measures
The GDPR requires appropriate technical and organizational measures to be implemented to ensure the security of personal data. This may include the use of encryption, pseudonymization of data, enhanced computer security protocols, and processes to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
7. Raise awareness and train staff
For better collaboration, it is crucial to train all employees on the principles of the GDPR and good data protection practices. Each employee handles personal data in the course of their duties. Therefore, commercial, HR, marketing, legal, etc., departments must contribute to the collective effort of identifying and processing data. Regular training sessions can help raise awareness among employees about the risks and responsibilities associated with data processing.
Here are our best tips for engaging your employees:
- Identify obstacles and training needs of the teams.
- Organize targeted training actions for different segments of employees.
- Monitor the progress of each team.
- Regularly remind them of good GDPR practices.
8. Implement data breach management procedures
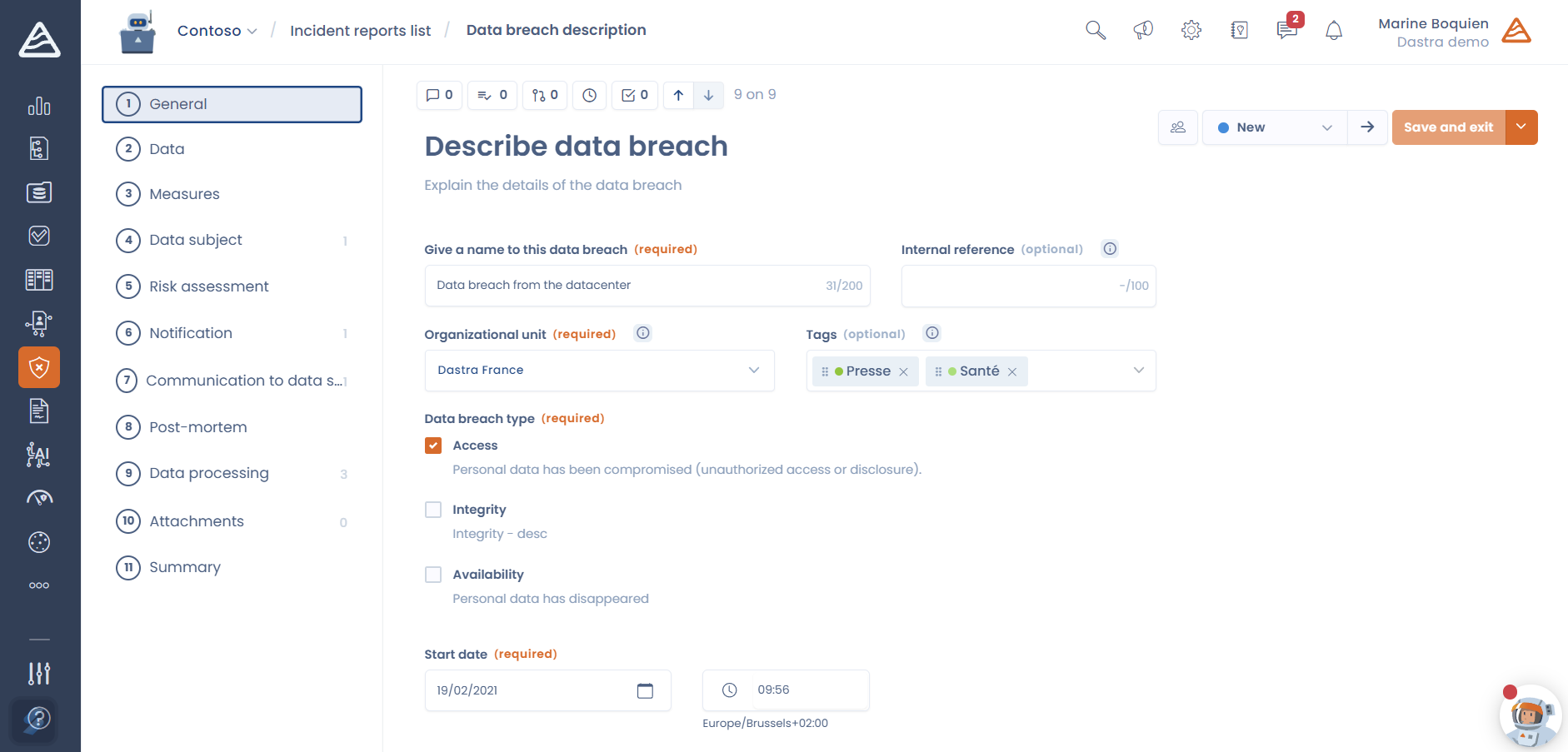
The GDPR requires notifying any data breach to the competent data protection authority within 72 hours, unless the breach is unlikely to result in a risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals.
It is therefore essential to have procedures in place to detect, report, and manage data breaches.
With Dastra, Manage your data breach register and improve your security.
9. Facilitate the exercise of individuals' rights
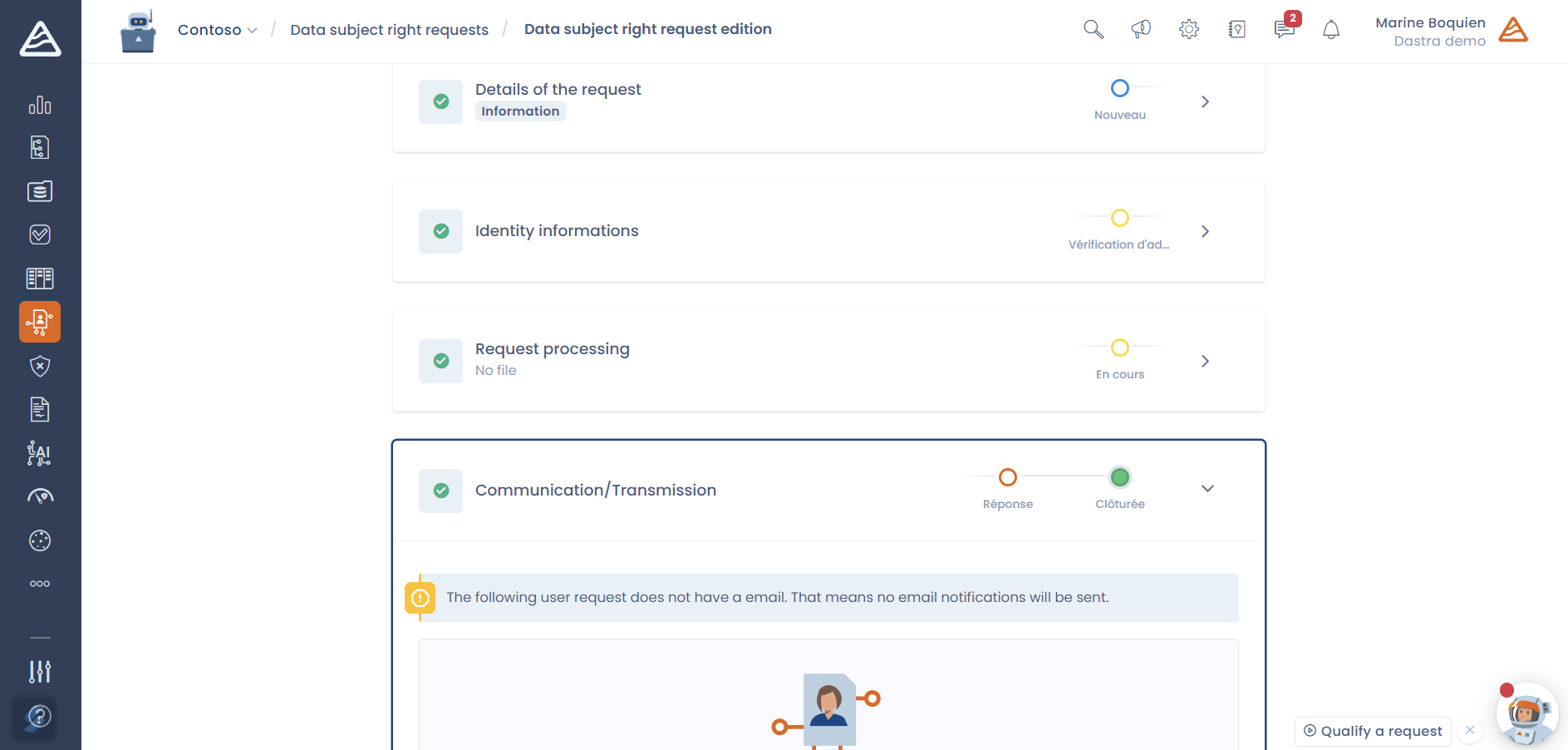
Individuals have specific rights regarding their personal data, such as the right of access, rectification, erasure, and data portability. One of the key elements of the GDPR is to give individuals control over their personal information. For this reason, each person has specific rights regarding their personal data:
- Right of access: Allows a user to know the progress of their data processing.
- Right of rectification: Allows modification and correction of personal data.
- Right to object: Allows to object to the use of their data for a specific purpose.
- Right to erasure or right to be forgotten: Enables obtaining the erasure of personal data.
- Right to restriction: Allows temporarily stopping the use of data.
- Right to data portability: Allows a person to retrieve part of their data in a readable format for personal use or to transmit it to another organization.
- Right to human intervention: Allows requesting human intervention in case of profiling.
Companies must establish procedures to enable individuals to easily exercise these rights.
For this, it is necessary to establish practical methods (online form, dedicated contacts), an effective internal process for handling requests, and a comprehensible and accessible response process for the individuals concerned.
With Dastra, automate the management of data subject requests!
10. Document compliance
Documentation is a key aspect of the GDPR. Companies must keep records of their data processing activities, risk assessments, implemented security measures, and evidence of compliance. This documentation may be requested by data protection authorities.
Choosing a suitable GDPR tool
Complying with the GDPR may seem complex, but by following these steps, you can effectively structure your approach as a company and reduce the risks of non-compliance.
The key is to make data protection a priority and integrate GDPR compliance into the company culture.
And for that, we invite you to choose a GDPR tool adapted to your needs! Contact our experts!
