Why compliance management has become a strategic challenge (and how to escape the chaos)
For a long time, regulatory compliance was seen as a one-off exercise.
A GDPR project here, an audit response there, a few shared Excel files… and then everyone moved on.
That time is over.
An unprecedented regulatory explosion
Cybersecurity, privacy, AI, information security, operational resilience…
The number of regulations impacting organizations is exploding, across increasingly interconnected domains:
GDPR, UK GDPR, CCPA / CPRA
NIS2, DORA
AI Act and internal AI governance requirements
ISO 27001, ISO 27701, SOC 2
Customer requirements, supplier audits, RFPs
Compliance is no longer a purely legal topic, it now directly impacts governance, risk management, commercial credibility, and overall organizational performance.
What we see in practice: compliance is often chaotic
In most organizations, implementing compliance is still experienced as a painful process.
What we observe again and again:
A proliferation of complex Excel files that are hard to read and quickly outdated
Compliance projects managed in silos, by regulation or by team
Discontinuous, reactive oversight, driven by audits or incidents
A lack of global visibility: no one really knows where things stand
The result? Efforts are duplicated, costs increase, and compliance remains reactive.
A paradigm shift: centralizing and managing compliance continuously
At Dastra, we strongly believe one thing: the real value is not in being compliant once, but in the ability to structure, manage, and demonstrate compliance over time.
This is the philosophy behind our Compliance module.
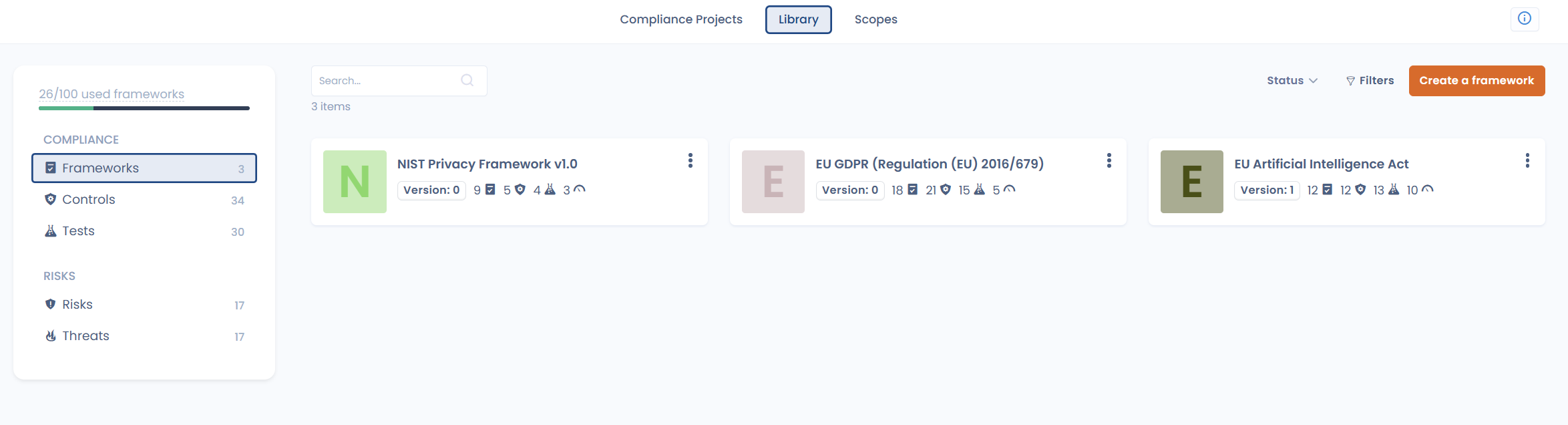
1. Structuring compliance: building a shared, reusable foundation
Rather than treating each regulation as a standalone project, Dastra allows you to centralize regulatory requirements, associated controls, and covered risks within a single reference framework.
You can build your own compliance frameworks using our regulatory framework editor,
or leverage our expert-designed libraries, including Privacy frameworks (e.g. GDPR), AI Governance (AI Act), ISO standards, Europrivacy, and many more.
You no longer have to start from scratch with every new obligation.
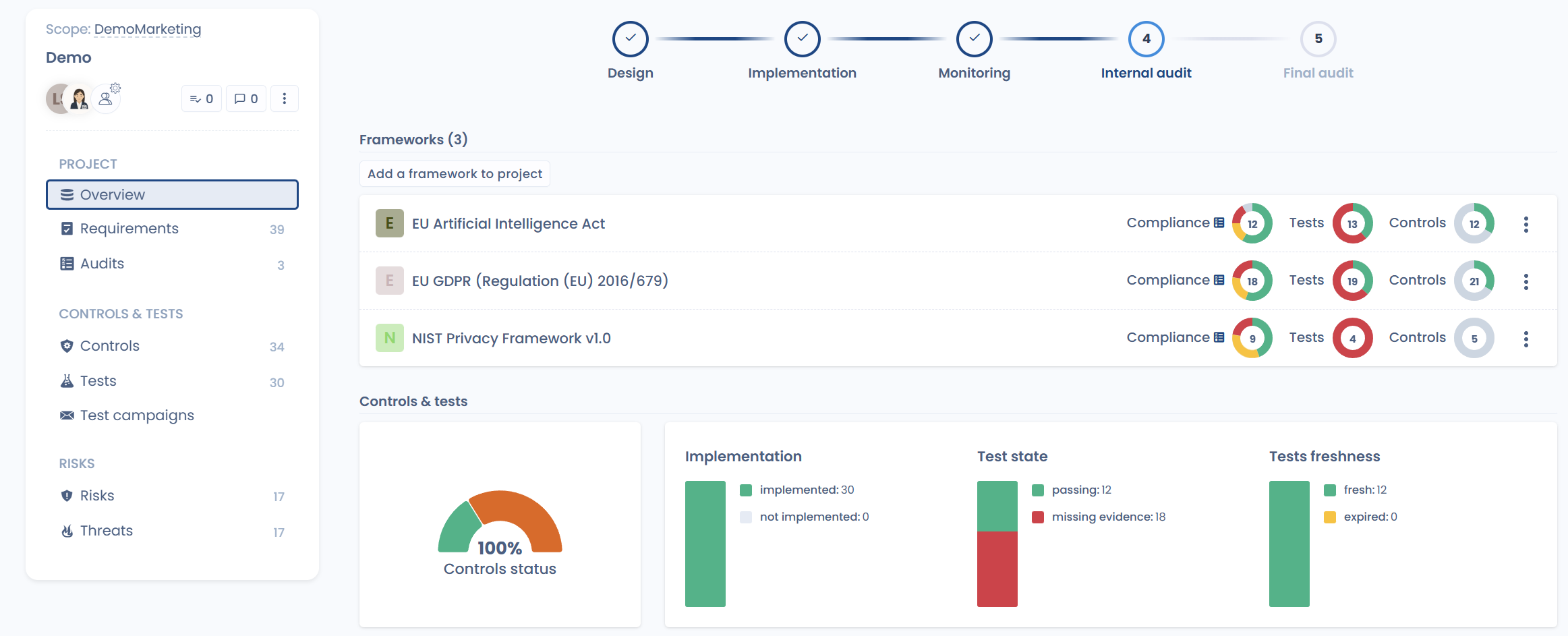 2. Sharing controls across multiple regulations
2. Sharing controls across multiple regulations
A common misconception is that each regulation requires a completely separate compliance setup.
In reality, many frameworks rely on the same core requirements: access management, data security, governance, incident handling, documentation, and traceability.
With Dastra, a single control can be mapped to multiple regulations. This allows you to share efforts, eliminate duplication, and significantly reduce hidden compliance costs.
Key concepts clarified
A control is a measure implemented to meet a regulatory requirement (for example: incident management).
A test verifies that the control is actually implemented and working as expected. It can be manual or automated, one-off or recurring. **Evidence is a tangible proof that a control was tested and respected: screenshots, documents, logs, reports, tool exports, etc. Without evidence, a control does not exist in the eyes of an auditor.
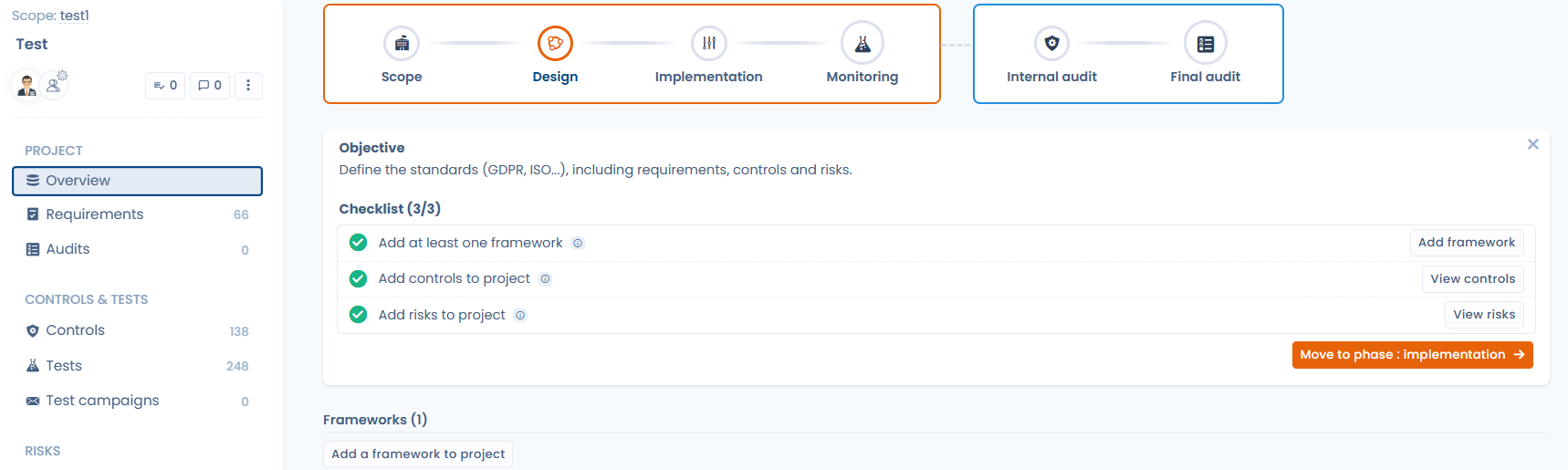
3. Managing compliance continuously (not just before audits)
Compliance is a living process.
With the Compliance module, you can:
Schedule regular control tests
Launch test campaigns and automated email requests to collect evidence from teams and users
Collect compliance evidence continuously
Monitor progress using clear, readable indicators
Automation helps, but it is not magic. It structures, schedules, and secures testing processes without replacing human judgment.
Compliance fully integrated into the Dastra platform
Within Dastra, you already manage key compliance assets such as:
Records of processing activities
Vendors and subprocessors
DPIAs
Vendor assessments
Risk analyses, and much more
The Compliance module builds directly on these existing assets, bringing everything together in a single, coherent environment where obligations, risks, and evidence are fully aligned.
Where to start when structuring your compliance program?
Not all organizations start from the same level of maturity. The key is to prioritize intelligently.
1. Define a realistic scope
Trying to address everything at once is rarely effective. Start by identifying the most critical subsidiaries or activities and appoint local compliance relays capable of owning controls.
2. Ask the right question: which regulations truly apply to you?
This depends on several factors:
Data location: compliance follows the data, not just headquarters
Industry: some obligations are sector-specific (e.g. healthcare)
Data types processed: sensitive data, minors’ data, large-scale processing
Organization size and role: employee count, revenue, controller vs processor
(e.g. DPO appointment, contractual obligations)
 3. Implementation: laying the foundations
3. Implementation: laying the foundations
The first step is to clearly define responsibilities and expectations.
You must identify who is responsible for each control (IT, security, legal, business teams), their scope, and their role in the overall compliance framework.
Without clear governance, even the best tools fail.
Next comes risk assessment, which helps identify which controls are truly critical based on data types, potential impacts, and regulatory requirements.
Finally, controls must be tested. Tests can be manual (document reviews, human verification), automated (where relevant), or hybrid.
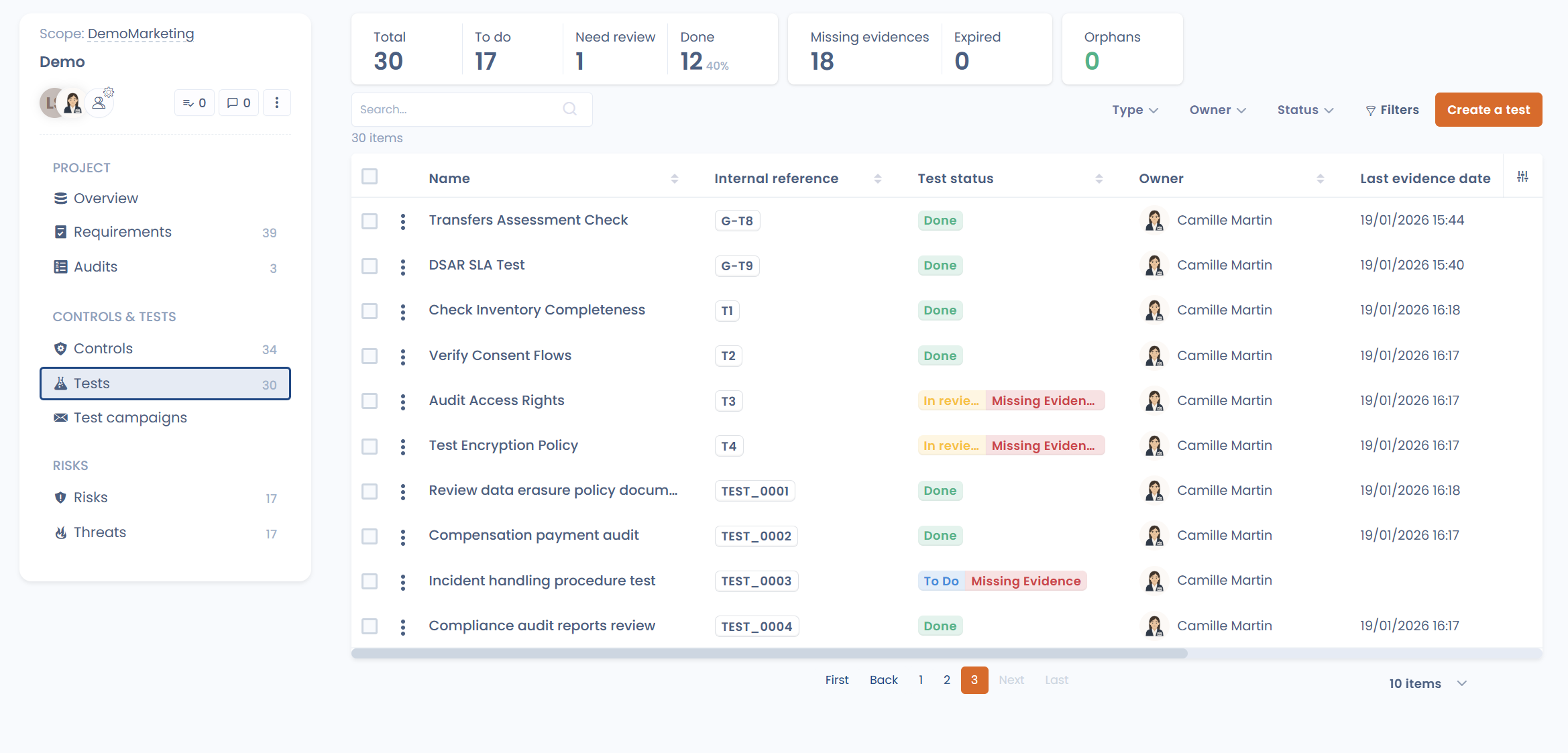 4. Monitoring (Run): keeping compliance alive
4. Monitoring (Run): keeping compliance alive
Once implemented, compliance enters its run phase. This is where many organizations struggle due to lack of tools or methodology.
Monitoring means: testing controls at defined intervals, collecting evidence for each test & tracking gaps over time.
Evidence is central: a control that is not tested or documented is, in practice, unverifiable.
Tracking gaps allows teams to detect weaknesses early, prioritize corrective actions, and avoid last-minute audit stress.
Compliance becomes controlled, not rushed.
5. Audit
Whether internal or external, an audit primarily aims to review existing practices, analyze gaps, and recommend improvements.
With continuous compliance management, organizations can:
reuse already collected evidence,
avoid time-consuming reconstructions,
drastically reduce audit-related time, stress, and costs.
Audits become a natural checkpoint within an already functioning system.
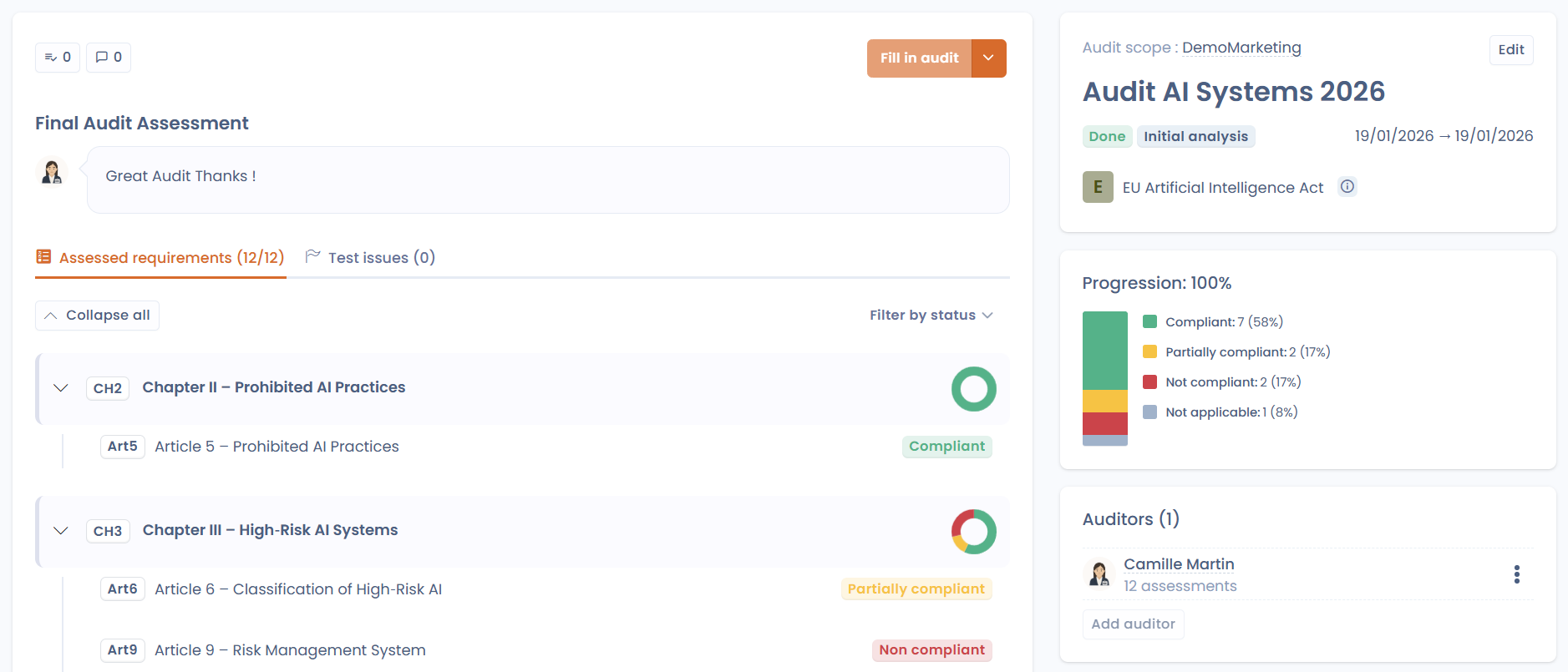
Conclusion: centralize, visualize, simplify
This is where the Compliance module truly shines.
The associated dashboard provides instant visibility into compliance project progress, implemented controls, completed tests & collected evidence.
Everything is centralized, readable, and actionable.
👉 To go further, explore the full documentation of the Compliance module and learn how to build sustainable compliance with Dastra.
Want to see the Compliance module in action? Book a demo with our teams.
